Vital Signs: Sea Level Rise Rapidly Accelerates Along the Southeast and Gulf Coasts
Researchers find record-breaking rates of sea level rise since 2010 — three times higher than the global average — from Cape Hatteras to the Gulf Coast.

Sea levels along the Southeast and Gulf coasts have been rapidly rising, reaching record-breaking rates over the past 12 years, according to a new study led by scientists at Tulane University. The research team detected rates of sea-level rise of about a half an inch per year since 2010.
“These rapid rates are unprecedented over at least the 20th-century, and they have been three times higher than the global average over the same period,” says Sönke Dangendorf, lead author, from the Department of River-Coastal Science and Engineering at Tulane.
The authors studied a combination of field and satellite measurements since 1900, pinpointing the individual contributors to the acceleration.
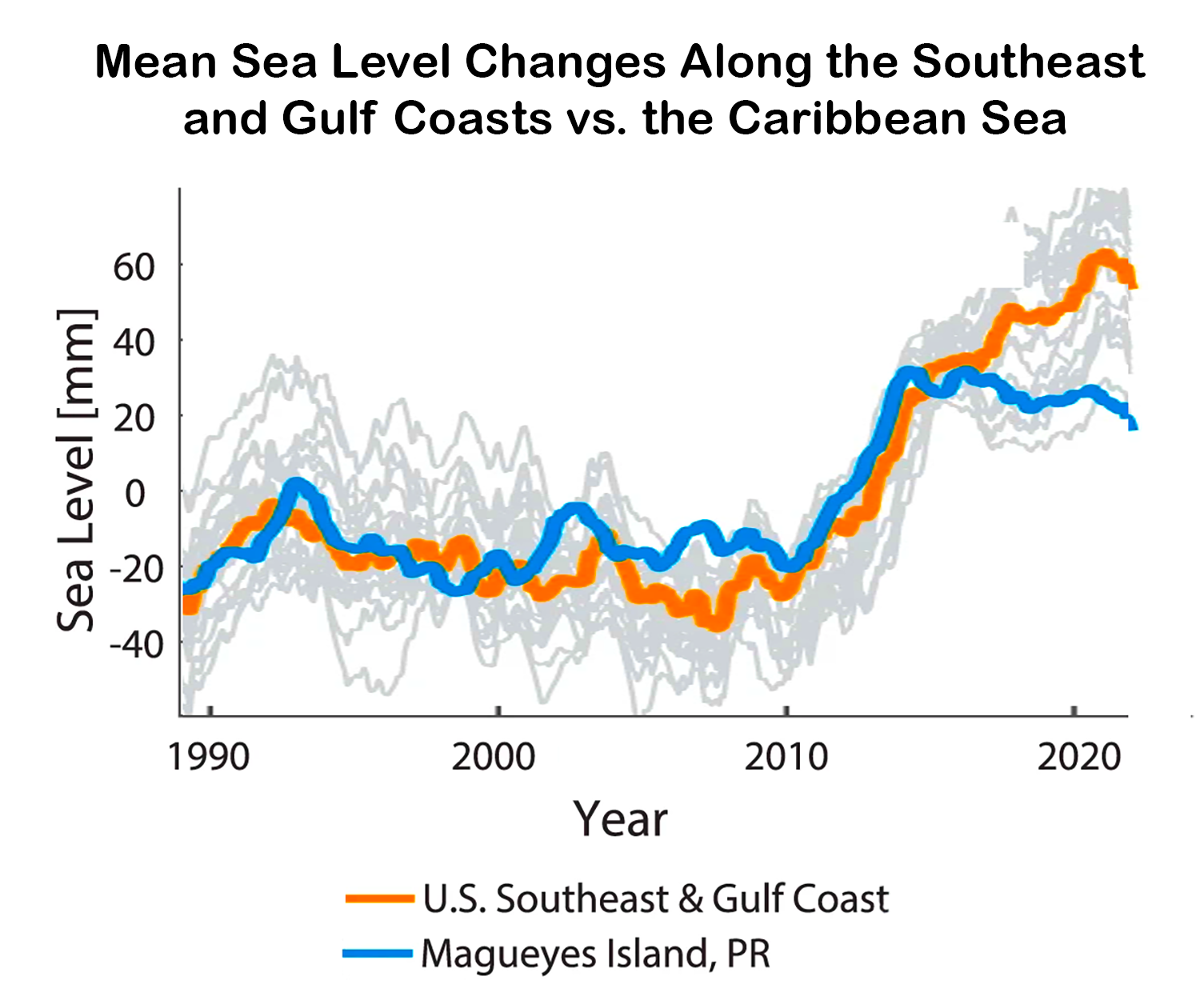
“We systematically investigated the different causes, such as vertical land motion, ice-mass loss, and air pressure, but none of them could sufficiently explain the recent rate,” says Noah Hendricks, co-author and a student at Old Dominion University. “Instead, we found that the acceleration is a widespread signal that extends from the coasts of the Gulf of Mexico up to Cape Hatteras in North Carolina and into the North Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Seas, which is indicative for changes in the ocean’s density and circulation.”
Over the past 12 years this entire area, known as the Subtropical Gyre, has been expanding primarily due to changing wind patterns and continued warming. Warmer water masses need more space and thus lead to a rise in sea level.
The scientists conclude that the rates will likely return to the values predicted by climate models in the coming decades.
“However, this is no reason to give the all-clear,” said Torbjörn Törnqvist, co-author, from the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences at Tulane.
“These high rates of sea-level rise have put even more stress on these vulnerable coastlines, particularly in Louisiana and Texas, where the land is also sinking rapidly.”
the full study in Nature Communications:
“Acceleration of U.S. Southeast and Gulf Coast Sea-Level Rise Amplified by Internal Climate Variability”
see also:
“Most of the World’s Salt Marshes Likely Will Be Underwater by 2100”
more from Coastwatch on climate change
Barri Bronston is assistant director of public relations at Tulane University and a former journalist for The Times-Picayune, earning awards from the Associated Press, the Louisiana Press Association, and the New Orleans Press Club, as well as sharing the Pulitzer Prize for Public Service for coverage of Hurricane Katrina and its aftermath.
adapted from a news story from AAAS
lead photo credit: NC State Photos.
- Categories:


